stormcloud unit production
In “Malaysian brain drain – don’t go chasing waterfalls” EMIR Research has presented the detailed results of a meta-analytical review of academic research on brain drain in the Malaysian context over the last decade — the long list of various “push” and “pull” factors that have been empirically linked to the Malaysian brain drain.
The core underlying problem behind all of these factors is poor governance, poor policy planning and/or execution (biased, corrupted, populistic, suboptimal, identity-based, divisive, haphazard, unfair, inconsistent, complacent, incompetent, regressive and simply outdated), which, as EMIR Research already underscored, is the single most critical variable we need to change before we see might start seeing the brain drain reversal.
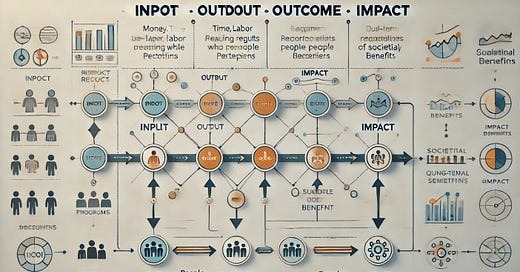
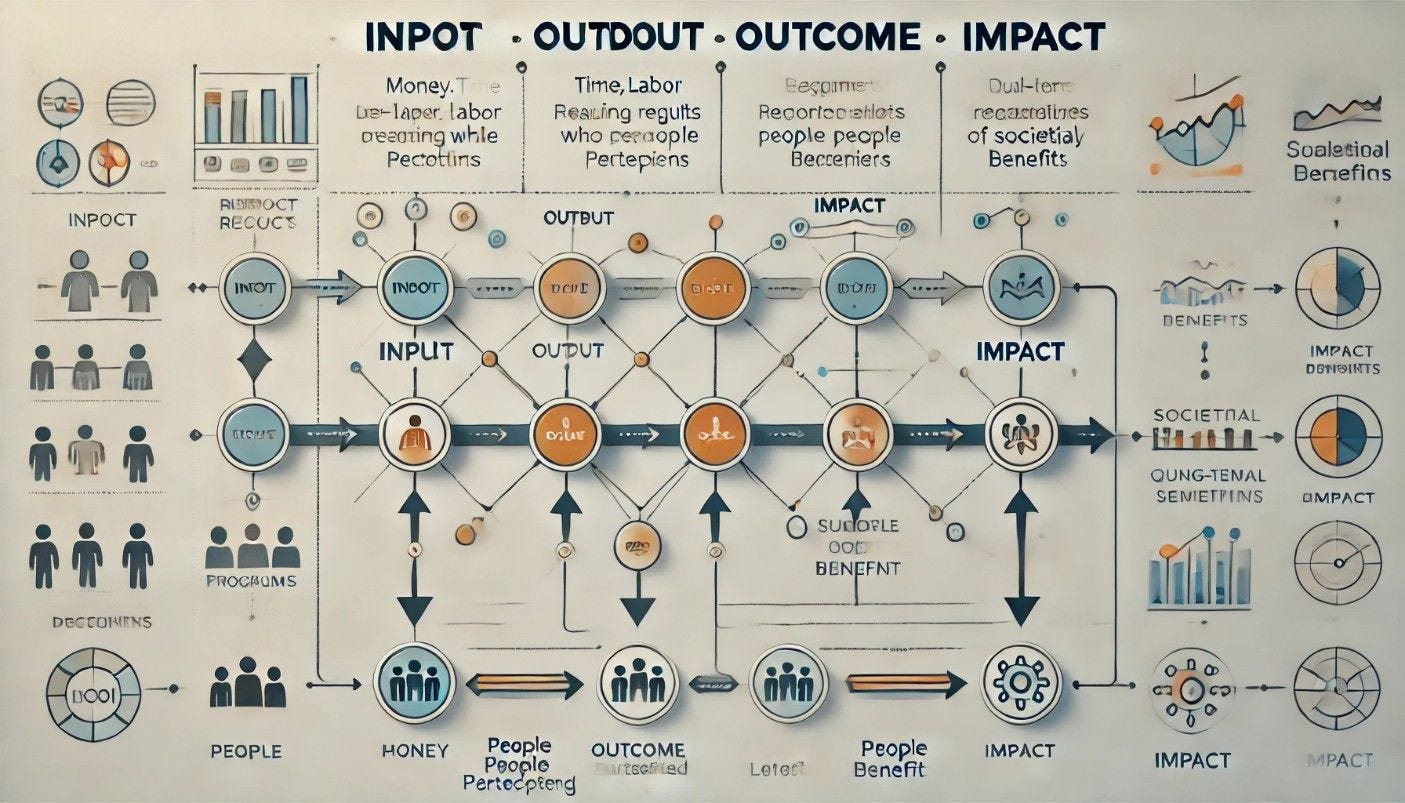
The IOOI framework is logical and robust reasoning (solely based on science and data) of the entire causal path from inputs (scarce resources / capitals) to outputs (tangible and intangible manifestation of intervention activities) to outcomes (real-world benefits / changed lives) and finally to impacts (higher-level intergenerational goals, if we speak in the context of a nation).
The key topics that are substaintially explored in literature cover:
1. Push and Pull Factors
Wage stagnation, limited career opportunities, and rigid socio-political structures are common push factors.
Neighboring countries offering better opportunities serve as pull factors.
2. Policy Responses
TalentCorp initiatives, Returning Experts Programme, and incentives for diaspora engagement.
The effectiveness of these policies has been widely debated in academic and policy literature.
3. Structural Issues
Ethnic-based policies, political instability, and lack of meritocracy are frequently cited as drivers of emigration.
4. Impact on Development
Loss of high-skilled workers affects Malaysia’s aspirations to transition into a high-income nation under Vision 2020 and beyond.
Academic Literature
1. Devadason, E. S., & Chan, W. M. (2014)
"Policies and issues in addressing brain drain in Malaysia: Perspectives of Malaysian diaspora."
Asian Journal of Social Science, 42(3-4), 391-423.
This article examines policies and challenges surrounding the Malaysian brain drain and highlights the perspectives of Malaysian expatriates.
2. Goh, K. L., & Wong, P. K. (2011)
"Brain drain and brain circulation: The case of Malaysia."
Singapore Economic Review, 56(03), 397-418.
Focuses on Malaysia’s attempts to mitigate brain drain through policies promoting brain circulation.
3. Tengku-Aizan, H., & Merican, M. I. M. (2016)
"Brain drain and brain gain: Malaysia’s experience."
Journal of Population Ageing, 9(3), 259-283.
Discusses migration patterns and their impact on Malaysia’s socioeconomic development, with a focus on skilled migration.
4. Abdul-Rahman, M. A., & Lee, H. A. (2020)
"Migration intentions among highly educated Malaysians: Why some stay and others leave."
Asian and Pacific Migration Journal, 29(1), 33-58.
Explores the motivations behind skilled Malaysians choosing to migrate or remain in the country.
---
Reports and Policy Briefs
1. World Bank (2011)
"Malaysia Economic Monitor: Brain Drain."
A comprehensive analysis of Malaysia's brain drain issue, its drivers, and the policy responses. The report emphasizes regional competition and the loss of talent to countries like Singapore.
2. Khazanah Research Institute (2018)
"The State of Households II: Work, Wages, and Wellbeing."
Discusses the relationship between wage stagnation, inequality, and migration trends among skilled Malaysians.
3. TalentCorp Malaysia (2015)
"Reversing Brain Drain: Returning Experts Programme (REP)."
Outlines the Malaysian government’s efforts to attract expatriates back to Malaysia through incentives and programs.
---
Books and Book Chapters
1. Yeoh, E. K. K., & Wong, D. (Eds.) (2019)
"Malaysian Perspectives on Human Capital Development."
Contains chapters addressing skilled migration and its impact on Malaysia’s human capital strategies.
2. Tham, S. Y., & Kam, K. Y. (2019)
"Migration of Highly Skilled Malaysians: Economics and Policy Implications."
In The Political Economy of Brain Drain and Talent Capture (Palgrave Macmillan).
Examines Malaysia’s challenges in retaining and attracting talent, focusing on regional competition and structural issues.
a stormcloud unit production